Industry Report Examines Plastic Pipe Materials and Health Impacts The latest report from Safe Piping Matters covers upcoming research showing commonly used plastic pipe materials can release significant amounts of microplastics and nanoplastics into plumbing systems. It also provides a look at current studies examining how these and other tiny plastic particles affect human health Read more
Safe Piping Matters

Industry Report Examines Plastic Pipe Materials and Health Impacts
The latest report from Safe Piping Matters covers upcoming research showing commonly used plastic pipe materials can release significant amounts of microplastics and nanoplastics into plumbing systems. It also provides a look at current studies examining how these and other tiny plastic particles affect human health, including impacts on the gut, lungs, brain, and reproductive organs, as well as increasing risks from related toxins and pathogens.

“The explosion of plastic pollution around the world continues to contaminate drinking water, food, and air with microplastics,” said Paul Hagar, Executive Director of Safe Piping Matters. “Our report shows why the plumbing industry needs to study the ways in which plastic pipe materials contribute to microplastic contamination.”
The report summarizes a study from Polish researchers who analyzed materials taken from water-transmission systems and found that plastic materials degrade “relatively quickly” as they age. Scans of the interior pipe surfaces showed peeling and flaking that released plastic particles into the water, adding to humans’ already significant exposure to ingested microplastics.
Plastic Pipes Microplastics and Health Impacts Report
The report also looks at issues such as chemical leaching in addition to shedding of micro- and nano- particles from common plastic pipe materials PVC (polyvinyl chloride), PE (polyethylene), PEX (cross-linked polyethylene), and CPVC (chlorinated polyvinyl chloride). It then reviews effects that medical studies have begun documenting on humans and/or lab animals, describing associations with cancer, cell death, tissue inflammation and damage, disruption of nervous function, reduced fertility, and other impacts.
“Architects, engineers, and contractors who care about the health and safety of building occupants should consider these issues when selecting piping materials,” says Hagar. “Emerging research does not support industry claims of rigorous testing standards and product safety.”

The release of a new Plumbing Specification Guide from Safe Piping Matters gives design and construction professionals an additional resource to guide evaluation and selection of pipe and fittings for drinking-water, drain/waste/vent, fire-suppression, and other critical piping applications. The new specification guide will also support municipalities and owners of individual buildings as they work to Read more
The release of a new Plumbing Specification Guide from Safe Piping Matters gives design and construction professionals an additional resource to guide evaluation and selection of pipe and fittings for drinking-water, drain/waste/vent, fire-suppression, and other critical piping applications. The new specification guide will also support municipalities and owners of individual buildings as they work to upgrade piping systems, including replacing infrastructure prioritized in recent federal programs.
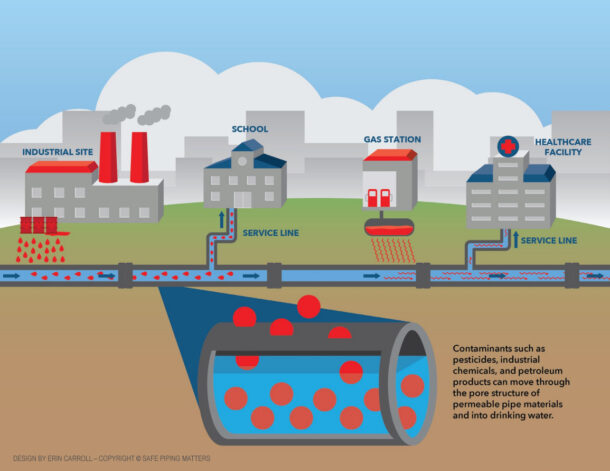
“Recent piping crises illustrate the importance of making thoughtful, informed choices,” said Paul Hagar, Executive Director of Safe Piping Matters. “Lead pipes are a prime example – a once widely available, affordable piping material deemed safe for use. Over the last decade, however, communities are investing billions of dollars and countless hours finding and replacing these toxic pipes. Piping systems represent a hidden opportunity to ensure the safety and health of occupants while also supporting the sustainability and resilience of a building.”
Available at SafePipingMatters.org/guide, the specification guide offers straightforward explanations and recommendations based on industry expertise, academic research, and real-world examples. Key topics include:
- System configurations
- Piping material strengths and weaknesses
- Plumbing codes, standards, and specification language
- Safety issues such as permeation, combustibility, and firestopping
- Health risks from leaching and toxicity
- Resilience factors that affect the lifespan of pipe
- Environmental issues related to production and disposal of pipe materials
- Emerging issues
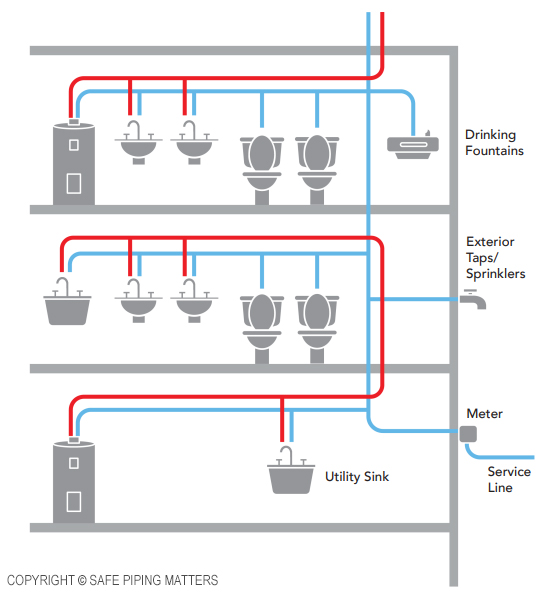
Safe Piping Matters is a nonprofit organization dedicated to providing design and construction professionals the best information on safe, resilient, and sustainable piping. We believe systems should not only improve building performance, but also protect the health of the people who live and work in them. Details at SafePipingMatters.org.
